En resumen, el contenido de los sólidos de la prensa de filtro es un material comprimido y deshidratado conocido como "torta de filtro", que se compone enteramente de las partículas sólidas suspendidas del lodo líquido inicial que se introdujo en la prensa. La composición química y física específica de estos sólidos depende completamente de la industria y del proceso particular del que se originó el lodo.
Una prensa de filtro no crea ni altera la naturaleza fundamental de los sólidos; es un dispositivo de separación mecánica. Piense en ella como una potente escurridora: el material sólido que sale es el mismo material sólido que entró, solo que con la mayor parte del líquido eliminado.
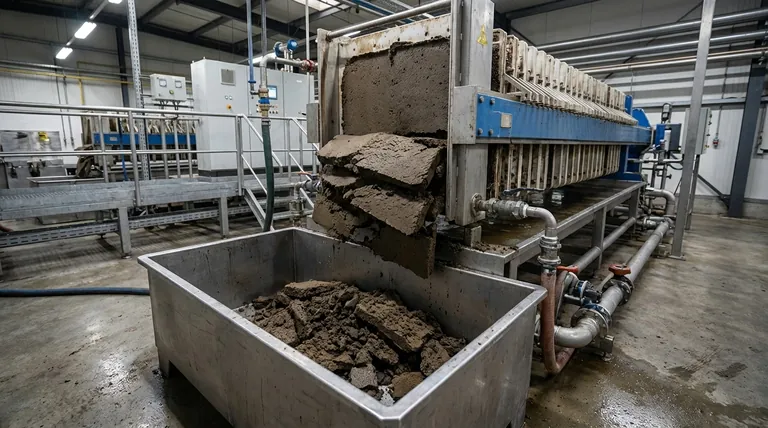

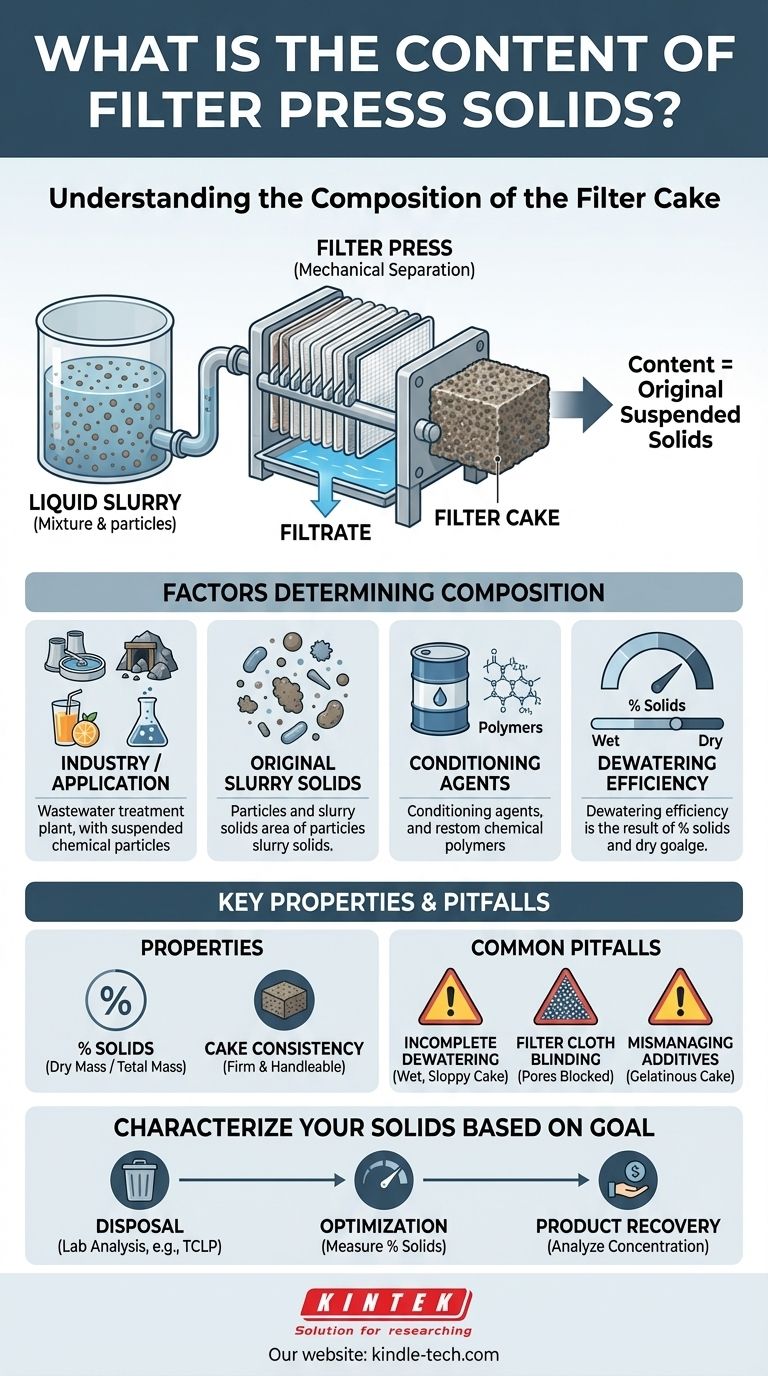
El principio fundamental: del lodo a la torta
Para comprender el contenido de los sólidos, primero debe comprender la entrada. Todo el proceso consiste en separar una mezcla en sus dos partes constituyentes.
La entrada: Lodo líquido
Una prensa de filtro comienza su trabajo con un lodo. Este es simplemente un término técnico para una mezcla donde las partículas sólidas están suspendidas, pero no disueltas, en un líquido. Este lodo es la fuente de todo lo que eventualmente se convertirá en la torta de filtro.
El proceso: Separación mecánica
La prensa de filtro bombea este lodo a alta presión a una serie de cámaras revestidas con telas filtrantes. El líquido, al poder pasar a través de los poros finos de la tela, sale de la prensa como un líquido claro llamado filtrado.
Las partículas sólidas, al ser demasiado grandes para pasar a través de la tela filtrante, quedan atrapadas y se acumulan dentro de las cámaras. A medida que el proceso continúa, estos sólidos atrapados se comprimen, forzando la salida de líquido adicional.
La salida: Torta de filtro
El producto final es la torta de filtro, una losa densa y semiseca de los sólidos comprimidos. El "contenido" de esta torta es, por lo tanto, idéntico al contenido de los sólidos que estaban suspendidos en el lodo original.
¿Qué determina la composición de los sólidos?
La composición de la torta de filtro se define por su origen. La misma máquina puede producir tipos de sólidos muy diferentes según la aplicación.
Aguas residuales municipales e industriales
En el tratamiento de aguas residuales, el lodo a menudo contiene lodos biológicos de las cuencas de aireación o precipitados químicos. La torta de filtro resultante se compone típicamente de materia orgánica, microorganismos y metales pesados precipitados (como hidróxidos metálicos) que se eliminaron del agua.
Minería y procesamiento de minerales
Una mina podría usar una prensa de filtro para deshidratar relaves (polvo de roca de desecho) para un almacenamiento más seguro o para concentrar minerales valiosos. La torta de filtro aquí consistiría en partículas finas de roca, arcilla y los minerales objetivo, como oro, cobre o zinc concentrados.
Producción de alimentos y bebidas
En el procesamiento de alimentos, una prensa de filtro podría clarificar jugos de frutas o vino. La torta resultante estaría hecha de pulpa, levadura y otros sólidos orgánicos. En el refinado de aceites comestibles, la torta consiste en tierra de blanqueo y otras impurezas eliminadas del aceite.
Fabricación de productos químicos
Las plantas químicas utilizan prensas de filtro para separar productos sólidos de reactivos líquidos o solventes. La torta de filtro podría ser un producto final valioso, como un pigmento, un catalizador precipitado o un compuesto químico específico.
Comprensión de las propiedades clave de los sólidos
Más allá de la composición química, las propiedades físicas de la torta son críticas para su manipulación y eliminación.
Porcentaje de sólidos (% de sólidos)
Esta es la medida más importante del rendimiento de la prensa de filtro. Representa la relación entre la masa seca de sólidos y la masa total de la torta. Una torta con 80% de sólidos se compone de 80% de material sólido y 20% de humedad residual. Un porcentaje de sólidos más alto indica una mejor deshidratación.
Consistencia de la torta
Un proceso optimizado produce una torta firme y sólida que se desintegra limpiamente cuando se abre la prensa. Esto facilita su recolección, manipulación y transporte. Un proceso deficiente da como resultado una torta "descuidada" o húmeda que es difícil de manejar.
El impacto de los agentes acondicionadores
A menudo, se añaden productos químicos al lodo antes de que entre en la prensa para mejorar el rendimiento. Estos agentes acondicionadores, como polímeros o cal, ayudan a que las partículas se agrupen para una separación más fácil. Es fundamental recordar que estos aditivos pasan a formar parte de la torta de filtro final y afectarán su composición, peso y características de eliminación.
Errores comunes a evitar
Lograr una torta de filtro de buena calidad requiere evitar problemas operativos comunes.
Deshidratación incompleta
Una torta húmeda y descuidada es el problema más frecuente. Esto a menudo es causado por un tiempo de ciclo insuficiente, una presión de alimentación incorrecta o el uso de una tela filtrante que no es apropiada para el tamaño de partícula específico de los sólidos.
Cegamiento de la tela filtrante
Si las partículas sólidas son extremadamente finas, pueden alojarse permanentemente en los poros de la tela filtrante, un fenómeno conocido como cegamiento. Esto restringe el flujo de agua, reduce drásticamente la eficiencia y da como resultado una torta húmeda y mal formada.
Mala gestión de los aditivos
Usar demasiado o el tipo incorrecto de polímero acondicionador puede crear una torta gelatinosa que retiene agua y es difícil de manejar. Además, cualquier aditivo debe tenerse en cuenta durante el análisis de eliminación, ya que ahora forman parte del flujo de residuos.
Cómo caracterizar sus sólidos
Su objetivo determina cómo debe abordar el análisis de su torta de filtro.
- Si su enfoque principal es la eliminación o el cumplimiento: Debe enviar una muestra representativa de la torta a un laboratorio para un análisis químico (como un Procedimiento de Lixiviación de Características de Toxicidad o TCLP) para clasificarla para un vertido adecuado.
- Si su enfoque principal es la optimización del proceso: Mida regularmente el porcentaje de sólidos de su torta para evaluar la eficiencia de la deshidratación y realice ajustes en la presión, los tiempos de ciclo o el acondicionamiento químico para maximizar la sequedad.
- Si su enfoque principal es la recuperación del producto: Debe analizar la torta para determinar la concentración de su material valioso objetivo para calcular el rendimiento de su proceso y asegurarse de que no está perdiendo producto.
En última instancia, comprender que la torta de filtro es un reflejo directo de su lodo de entrada es el primer paso para dominar su proceso de separación.
Tabla resumen:
| Factor clave | Impacto en el contenido de la torta de filtro |
|---|---|
| Industria/Aplicación | Define la composición química fundamental (ej., minería=minerales, aguas residuales=lodos). |
| Sólidos del lodo original | La torta se compone de estas partículas exactas, solo deshidratadas. |
| Agentes acondicionadores | Aditivos como los polímeros pasan a formar parte de la torta final, afectando sus propiedades. |
| Eficiencia de deshidratación | Medida por % de sólidos; un % más alto significa una torta más seca y estable. |
¿Necesita optimizar su proceso de filtración o caracterizar su torta de filtro?
Comprender el contenido y las propiedades precisas de los sólidos de su prensa de filtro es fundamental para una operación eficiente, una eliminación rentable o la maximización de la recuperación del producto. Los expertos de KINTEK se especializan en equipos y consumibles de laboratorio para analizar y optimizar los procesos de separación. Podemos ayudarle a seleccionar las herramientas adecuadas para medir el porcentaje de sólidos, analizar la composición de la torta y mejorar su eficiencia general.
Permítanos discutir su lodo específico y sus desafíos de filtración. Contacte a nuestro equipo hoy para encontrar la solución perfecta para sus necesidades de laboratorio.
Guía Visual
Productos relacionados
- Prensa Isostática en Caliente WIP Estación de Trabajo 300Mpa para Aplicaciones de Alta Presión
- Prensa de Calentamiento de Doble Placa para Laboratorio
- Prensa Hidráulica de Laboratorio Prensa para Pellets para Baterías de Botón
- Prensa Hidráulica Manual Calentada con Placas Calentadas para Prensa en Caliente de Laboratorio
- Máquina Prensadora Eléctrica de Tabletas de un Solo Punzón Prensa TDP para Polvo de Laboratorio
La gente también pregunta
- ¿Cuál es el trasfondo histórico del proceso de prensado isostático en caliente (HIP)? De las raíces nucleares al estándar industrial
- ¿Cuánta energía consume el prensado isostático en caliente? Desbloquee el ahorro neto de energía en su proceso
- ¿Cuál es el principio del prensado isostático en caliente? Lograr una densidad del 100% y un rendimiento superior
- ¿Qué es el proceso de material HIP? Logre una densidad y fiabilidad casi perfectas
- ¿Cuáles son algunas de las propiedades atractivas de los productos prensados isostáticamente en caliente? Lograr una densidad perfecta y un rendimiento superior



















