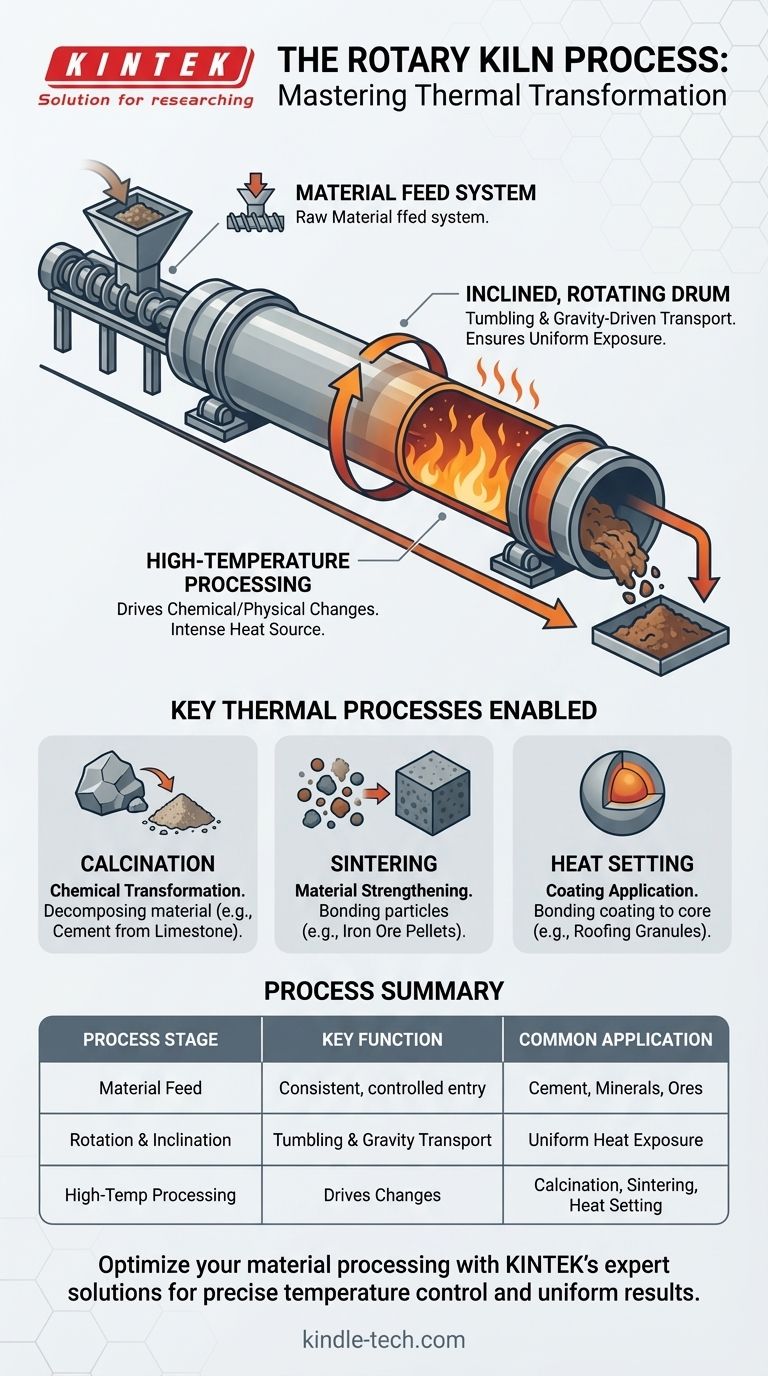
En esencia, el proceso del horno rotatorio implica alimentar continuamente material por el extremo superior de un cilindro grande, giratorio y ligeramente inclinado. A medida que el horno gira, el material se voltea y se mueve gradualmente hacia el extremo inferior debido a la gravedad. Esta acción de volteo asegura que el material se exponga uniformemente a temperaturas extremadamente altas, lo que impulsa reacciones químicas o cambios físicos específicos para producir un producto final transformado.
El principio fundamental de un horno rotatorio es utilizar el movimiento mecánico —rotación e inclinación— para lograr un procesamiento térmico altamente controlado y uniforme de los materiales a escala industrial y continua.

La Mecánica Central: Cómo Funciona un Horno Rotatorio
Un horno rotatorio no es un componente único, sino un sistema, con el tambor giratorio, o reactor, en su centro. Comprender cómo se mueve el material a través de este sistema es clave para entender el proceso.
El Sistema de Alimentación de Material
El material entra al horno a través de una canaleta de alimentación o un alimentador de tornillo en el extremo elevado. Este sistema está diseñado para un flujo constante y cuantitativo de materia prima. El diseño suele ser robusto y fabricado con aleaciones resistentes al calor para evitar la acumulación de material y soportar altas temperaturas.
El Tambor Inclinado y Giratorio
El horno en sí es un cilindro largo posicionado en un ligero ángulo horizontal. Esta inclinación es fundamental, ya que utiliza la gravedad para mover el material desde el extremo de alimentación hasta el extremo de descarga.
La rotación del tambor cumple un doble propósito: voltea el material, asegurando que cada partícula se exponga uniformemente a la fuente de calor, y ayuda a transportar el material a lo largo del horno.
Procesamiento a Alta Temperatura
La función principal del horno es crear un ambiente de temperatura ultra alta. Este calor intenso es el catalizador para todo el proceso, proporcionando la energía necesaria para que ocurran diversas reacciones termodinámicas o cinéticas dentro del lecho de material.
Procesos Térmicos Clave Habilitados por el Horno
La versatilidad del horno rotatorio proviene de su capacidad para facilitar una amplia gama de procesos térmicos mediante el control de la temperatura, la atmósfera y el tiempo de residencia.
Calcinación (Transformación Química)
La calcinación es un proceso que utiliza calor intenso para impulsar reacciones químicas, a menudo descomponiendo un material. El ejemplo más común es calentar piedra caliza para producir cal y dióxido de carbono, un paso fundamental en la fabricación de cemento.
Sinterización (Fortalecimiento del Material)
La sinterización implica calentar un material a una temperatura justo por debajo de su punto de fusión. Esto hace que las partículas se unan y se fusionen, lo que aumenta significativamente la resistencia y densidad del material. Esto se utiliza frecuentemente para la peletización de mineral de hierro y la creación de apuntalantes de alta resistencia para la industria del petróleo y el gas.
Fijación por Calor (Aplicación de Recubrimiento)
En la fijación por calor, un mineral central se recubre con otro material. El horno calienta los materiales para que el recubrimiento se vuelva viscoso y se adhiera firmemente al núcleo. Esta técnica es esencial en la fabricación de gránulos para techos, donde los pigmentos de color se fusionan a una base de granito.
Otras Funciones Críticas
El ambiente controlado de un horno rotatorio también lo hace ideal para otras funciones, incluyendo el secado, la combustión orgánica, la incineración de residuos y la calcinación reductora para cambiar el estado químico de los metales.
Comprensión de las Consideraciones de Ingeniería
La eficacia de un horno rotatorio no es accidental; es el resultado de una ingeniería precisa adaptada a un material específico y al resultado deseado.
La Importancia del Dimensionamiento Correcto
Dimensionar un horno rotatorio es una tarea compleja que combina análisis térmico, ingeniería química y experiencia práctica. No existe una solución única para todos.
Los diseñadores deben determinar el diámetro y la longitud ideales del horno basándose en factores críticos para garantizar que se cumplan los objetivos del proceso de manera eficiente y efectiva.
Factores Clave de Dimensionamiento
Las dimensiones finales de un horno dependen de un equilibrio de variables. Estas incluyen la capacidad requerida (cuánto material necesita ser procesado), el tiempo de residencia (cuánto tiempo debe permanecer el material en el horno), la tasa de alimentación máxima y las propiedades químicas y físicas específicas del material que se procesa.
Adaptar el Proceso a su Objetivo
La función térmica específica que emplee depende enteramente de su objetivo final para el material.
- Si su enfoque principal es la descomposición química para crear un nuevo compuesto: La calcinación es el proceso central, como se ve en la fabricación de cemento.
- Si su enfoque principal es aumentar la resistencia y densidad de un material: La sinterización es el método para unir partículas, esencial para productos como los pellets de mineral de hierro.
- Si su enfoque principal es aplicar un recubrimiento duradero y fusionado por calor: La fijación por calor proporciona el ambiente controlado para unir un material a otro, como en los gránulos para techos.
En última instancia, el proceso del horno rotatorio es una herramienta térmica potente y adaptable, diseñada para satisfacer una amplia gama de necesidades de transformación de materiales industriales.
Tabla Resumen:
| Etapa del Proceso | Función Clave | Aplicación Industrial Común |
|---|---|---|
| Alimentación del Material | Entrada consistente y controlada de materia prima | Cemento, minerales, menas |
| Rotación e Inclinación | Volteo y transporte impulsado por gravedad | Asegura una exposición uniforme al calor |
| Procesamiento a Alta Temperatura | Impulsa cambios químicos/físicos | Calcinación, sinterización, fijación por calor |
Optimice el procesamiento de sus materiales con las soluciones expertas de KINTEK. Ya sea que se dedique a la calcinación, la sinterización o la fijación por calor, nuestros equipos de laboratorio especializados y consumibles están diseñados para satisfacer las rigurosas demandas de la transformación térmica industrial. Permita que nuestro equipo le ayude a lograr un control preciso de la temperatura y resultados uniformes. Contáctenos hoy para discutir cómo podemos apoyar las necesidades específicas de su laboratorio.
Guía Visual
Productos relacionados
- Planta de Horno de Pirólisis de Horno Rotatorio Eléctrico Máquina Calcinadora Horno Rotatorio Pequeño Horno Giratorio
- Horno Rotatorio Eléctrico Pequeño Horno Rotatorio para Regeneración de Carbón Activado
- Horno Rotatorio de Inclinación de Vacío de Laboratorio Horno de Tubo Giratorio
- Horno de Tubo Rotatorio Continuo Sellado al Vacío Horno de Tubo Giratorio
- Horno de Mufla de Laboratorio con Elevación Inferior
La gente también pregunta
- ¿Por qué hay cadenas dentro de un horno rotatorio? Aumente la eficiencia y el control con el intercambio de calor interno
- ¿Qué hace un calcinador rotatorio? Logre un procesamiento térmico uniforme para sus materiales
- ¿Cuáles son los diferentes tipos de incineradores de horno rotatorio? Encuentre el diseño adecuado para su flujo de residuos
- ¿Cuáles son los dos componentes del movimiento de materiales dentro de un cilindro giratorio? Optimice el rendimiento de su horno y secador
- ¿Cuáles son las ventajas del horno de horno rotatorio? Logre una uniformidad y eficiencia superiores
- ¿Cuáles son las condiciones operativas de la pirólisis? Domine el calor, el reactor y la materia prima para obtener resultados óptimos
- ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre la pirólisis por microondas y la pirólisis convencional? Elija el método de calentamiento adecuado para su proceso
- ¿Qué es la zona de calcinación en el horno rotatorio? La clave para una transformación química eficiente



















