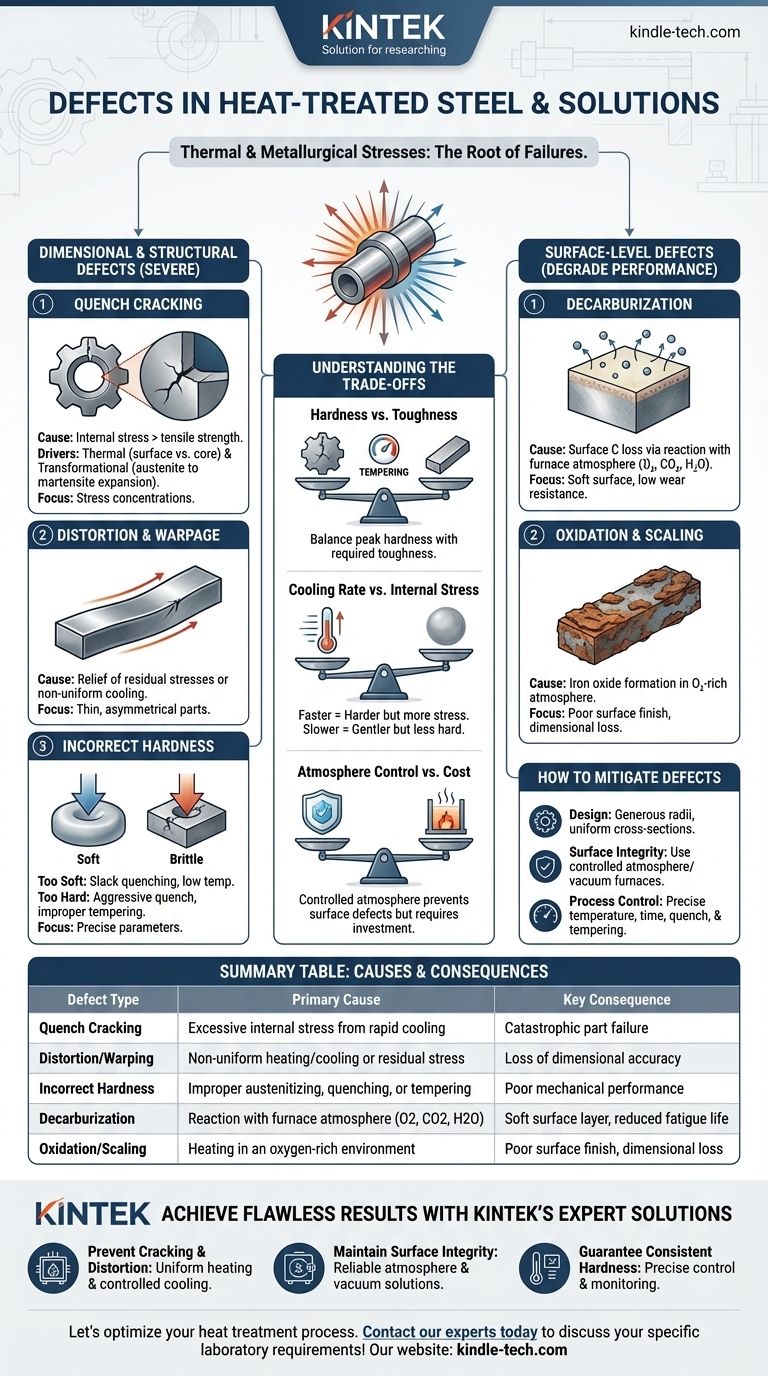
Los defectos en el acero tratado térmicamente son causados principalmente por las inmensas tensiones térmicas y metalúrgicas introducidas durante el calentamiento y el enfriamiento rápido. Los defectos más comunes son el agrietamiento, la distorsión (deformación), cambios superficiales indeseables como la descarburación y la formación de cascarilla, y el fallo en alcanzar la dureza o microestructura objetivo. Estas fallas no son aleatorias, sino consecuencias directas de parámetros de proceso mal controlados.
Los defectos del tratamiento térmico son resultados predecibles de la tensión térmica, las transformaciones de fase y las reacciones químicas atmosféricas. Prevenirlos depende del control riguroso de la velocidad de cambio de temperatura, la atmósfera del horno y la geometría de la pieza desde la etapa de diseño en adelante.

Fallos Dimensionales y Estructurales
Los defectos más graves comprometen la integridad mecánica y la precisión dimensional del componente, a menudo dejándolo inutilizable.
Agrietamiento por Temple (Quench Cracking)
El agrietamiento por temple es el defecto de tratamiento térmico más crítico. Ocurre cuando las tensiones internas del temple superan la resistencia a la tracción última del material.
Esto es impulsado por dos fuerzas principales: la tensión térmica resultante de que la superficie se enfríe mucho más rápido que el núcleo, y la tensión transformacional derivada de la expansión que ocurre cuando la austenita se transforma en martensita frágil.
Las grietas generalmente se originan en puntos de concentración de tensión, como esquinas afiladas, chaveteros o cambios bruscos en la sección transversal de la pieza.
Distorsión y Deformación (Warpage)
La distorsión es un cambio irreversible en el tamaño o la forma de un componente que ocurre durante el tratamiento térmico.
A menudo es causada por la liberación de tensiones residuales impuestas durante pasos de fabricación previos (como el mecanizado) o por un calentamiento y enfriamiento no uniformes. Las piezas delgadas, largas o asimétricas son particularmente susceptibles a la deformación.
Dureza Incorrecta
Lograr la dureza correcta es a menudo el objetivo principal, y el fallo en este aspecto puede deberse a varios factores.
Una pieza demasiado blanda puede ser el resultado de una temperatura o tiempo de austenización insuficientes, o un temple demasiado lento para la templabilidad del acero (lo que se conoce como temple flojo o slack quenching).
Por el contrario, una pieza demasiado dura y frágil es a menudo el resultado de un temple demasiado agresivo o, más comúnmente, de un paso de revenido inadecuado o omitido después del endurecimiento.
Defectos a Nivel Superficial
Estos defectos degradan la superficie del acero, comprometiendo su rendimiento en aplicaciones que requieren alta resistencia al desgaste o a la fatiga.
Descarburación
La descarburación es la pérdida de carbono de la superficie del acero. Este es un problema significativo porque el carbono es el elemento principal responsable de la dureza en el acero.
Es causada por una reacción química entre el acero y la atmósfera del horno (oxígeno, dióxido de carbono, vapor de agua) a altas temperaturas. El resultado es una capa superficial blanda y débil que reduce drásticamente la resistencia al desgaste y la vida a la fatiga.
Oxidación y Formación de Cascarilla (Scaling)
La oxidación es la formación de una capa de óxido de hierro (cascarilla) en la superficie del componente cuando se calienta en una atmósfera rica en oxígeno.
Esta cascarilla provoca un mal acabado superficial y una pérdida de precisión dimensional. También puede aislar la pieza, lo que lleva a un temple no uniforme y potencialmente enmascara defectos subyacentes más graves, como las grietas por temple.
Comprender las Compensaciones (Trade-offs)
Seleccionar un proceso de tratamiento térmico siempre implica equilibrar factores en competencia. Comprender estas compensaciones es clave para prevenir defectos.
Dureza vs. Tenacidad
La compensación fundamental en el tratamiento térmico es que los procesos que crean una dureza extrema, como el temple, también crean una microestructura frágil (martensita sin revenir).
El revenido es el paso post-temple esencial que reduce esta fragilidad y la tensión interna, confiriendo tenacidad. Sin embargo, este proceso también reduce la dureza máxima. El arte reside en encontrar el equilibrio preciso requerido para la aplicación.
Velocidad de Enfriamiento vs. Tensión Interna
Una velocidad de enfriamiento más rápida es más efectiva para lograr la dureza total, especialmente en aceros de baja aleación.
Sin embargo, un temple rápido (por ejemplo, usando agua o salmuera) genera inmensos gradientes térmicos y tensión interna, aumentando drásticamente el riesgo de distorsión y agrietamiento. Un temple más lento (por ejemplo, usando aceite o gas) es más suave, pero puede que no alcance la dureza máxima.
Control de Atmósfera vs. Costo
Utilizar una atmósfera controlada (como vacío, nitrógeno o argón) previene completamente la descarburación y la oxidación, produciendo una pieza limpia y brillante.
Sin embargo, estos procesos requieren equipos más sofisticados y costosos en comparación con el calentamiento en un horno de aire abierto. El costo debe justificarse por los requisitos superficiales del componente.
Cómo Mitigar los Defectos del Tratamiento Térmico
Prevenir defectos requiere un enfoque sistemático centrado en el diseño, la selección de materiales y el control preciso del proceso.
- Si su enfoque principal es prevenir el agrietamiento y la distorsión: Diseñe piezas con radios generosos y secciones transversales uniformes, y seleccione un medio de temple menos severo apropiado para la templabilidad del acero.
- Si su enfoque principal es mantener la integridad superficial: Utilice hornos de atmósfera controlada (p. ej., vacío, gas inerte) o recubrimientos protectores para prevenir la descarburación y la formación de cascarilla.
- Si su enfoque principal es lograr una dureza constante: Asegure un control preciso de la temperatura de austenización, el tiempo de mantenimiento y la agitación del temple, y siempre realice un ciclo de revenido adecuado posteriormente.
Un tratamiento térmico exitoso es un proceso de ingeniería controlado donde la previsión en el diseño y la precisión en la ejecución determinan la calidad final del componente.
Tabla Resumen:
| Tipo de Defecto | Causa Principal | Consecuencia Clave |
|---|---|---|
| Agrietamiento por Temple | Tensión interna excesiva por enfriamiento rápido | Fallo catastrófico de la pieza |
| Distorsión/Deformación | Calentamiento/enfriamiento no uniforme o tensión residual | Pérdida de precisión dimensional |
| Dureza Incorrecta | Austenización, temple o revenido inadecuados | Rendimiento mecánico deficiente |
| Descarburación | Reacción con la atmósfera del horno (O2, CO2, H2O) | Capa superficial blanda, vida a la fatiga reducida |
| Oxidación/Cascarilla | Calentamiento en un ambiente rico en oxígeno | Mal acabado superficial, pérdida dimensional |
Logre Resultados Impecables con las Soluciones Expertas de KINTEK
Elimine los costosos defectos del tratamiento térmico y asegúrese de que sus componentes de acero cumplan con los más altos estándares de dureza, durabilidad y precisión dimensional. KINTEK se especializa en equipos y consumibles de laboratorio premium, proporcionando los hornos precisos, los sistemas de control de atmósfera y el soporte experto que su laboratorio necesita para perfeccionar su procesamiento térmico.
Le ayudamos a:
- Prevenir el Agrietamiento y la Distorsión: Con equipos diseñados para un calentamiento uniforme y un enfriamiento controlado.
- Mantener la Integridad Superficial: Mediante soluciones fiables de hornos de vacío y atmósfera controlada.
- Garantizar una Dureza Consistente: Con control preciso de la temperatura y herramientas de monitoreo, y siempre realizando un ciclo de revenido adecuado.
Optimicemos su proceso de tratamiento térmico. ¡Contacte a nuestros expertos hoy para discutir sus requisitos específicos de laboratorio!
Guía Visual
Productos relacionados
- Horno de Tratamiento Térmico al Vacío con Revestimiento de Fibra Cerámica
- Horno de Sinterización y Tratamiento Térmico al Vacío de Tungsteno de 2200 ℃
- Horno de tratamiento térmico al vacío y horno de fusión por inducción de levitación
- Horno de Tratamiento Térmico al Vacío de Molibdeno
- Horno de Sinterización y Soldadura Fuerte por Tratamiento Térmico al Vacío
La gente también pregunta
- ¿Puedo aspirar el interior de mi horno de calefacción? Una guía para la limpieza segura por bricolaje frente al servicio profesional
- ¿Qué materiales se utilizan en un horno de vacío? Una guía sobre los materiales de la zona caliente y los metales procesados
- ¿Qué es la alta temperatura de un horno de vacío? Descubra el rango para su procesamiento de materiales
- ¿Qué hace un horno de vacío? Lograr un tratamiento térmico de alta pureza para componentes superiores
- ¿Qué es un horno de vacío? La guía definitiva para el procesamiento térmico sin contaminación



















