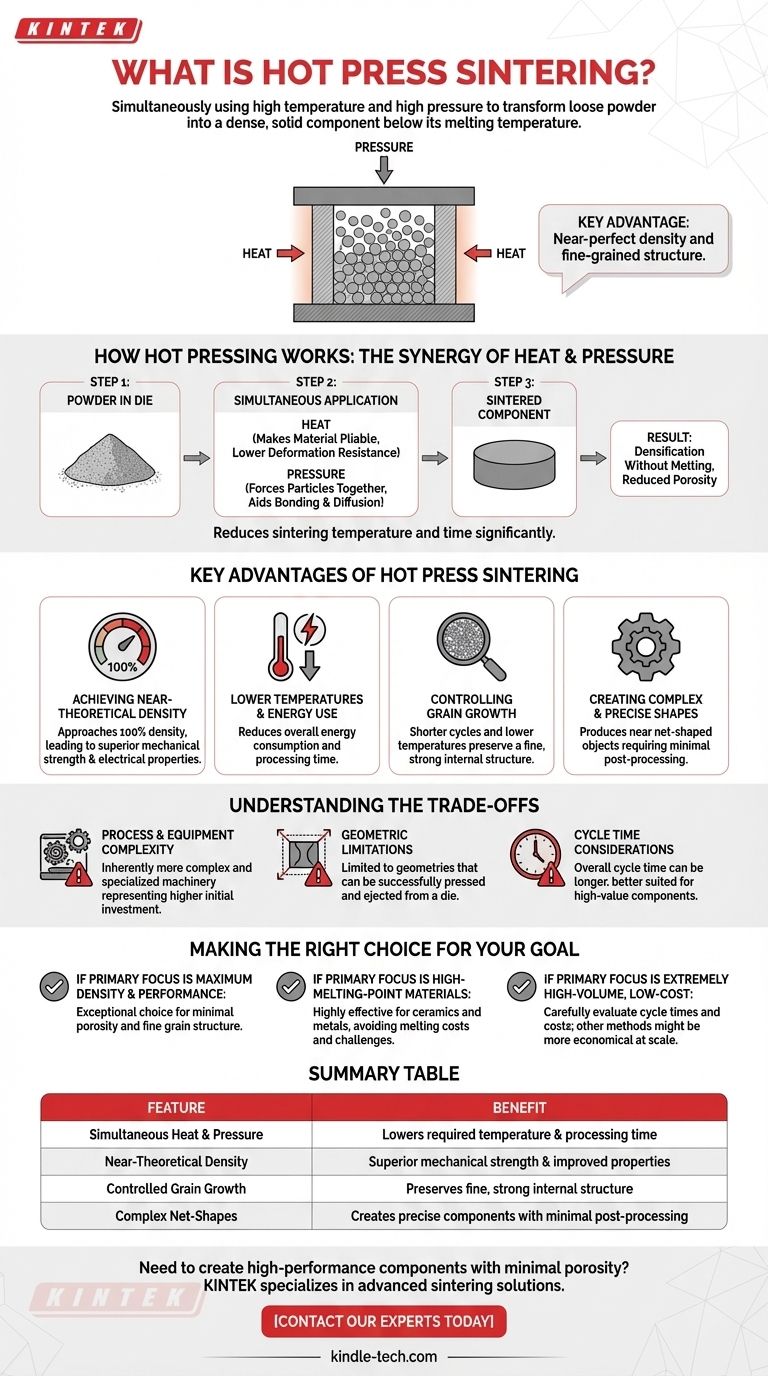
En esencia, la sinterización por prensado en caliente es un proceso de fabricación que utiliza alta temperatura y alta presión simultáneamente para transformar un polvo suelto en un componente denso y sólido. A diferencia de la fusión tradicional, el material se calienta hasta un punto por debajo de su temperatura de fusión, lo que permite que las partículas se fusionen bajo fuerza mecánica. Esta acción dual es la clave de su eficacia.
La ventaja central de la sinterización por prensado en caliente es su capacidad para producir materiales con una densidad casi perfecta y una estructura interna de grano fino. Al aplicar calor y presión al mismo tiempo, reduce la temperatura y el tiempo de procesamiento requeridos, lo que a su vez conduce a propiedades finales superiores en comparación con muchos otros métodos.

Cómo funciona el prensado en caliente: la sinergia de calor y presión
Para comprender la sinterización por prensado en caliente, es crucial ver cómo sus dos elementos centrales —calor y presión— trabajan juntos para lograr un resultado que ninguno podría lograr con la misma eficacia por sí solo.
El objetivo fundamental: densificación sin fusión
El principio básico de cualquier proceso de sinterización es reducir los espacios porosos entre las partículas individuales de un polvo. Esto compacta el material en un bloque sólido con una resistencia y otras propiedades significativamente mejoradas.
La diferencia clave: aplicación simultánea
Los métodos tradicionales podrían implicar "prensado en frío" de un polvo para darle forma y luego calentarlo en un paso de horno separado. El prensado en caliente integra estos dos pasos en una sola operación.
El calor aplicado hace que el material en polvo sea más maleable, casi como un termoplástico. En este estado, el material tiene una resistencia a la deformación mucho menor.
Ayudando a la transferencia de masa y la unión
Este estado termoplástico permite que la presión aplicada simultáneamente sea mucho más efectiva. Fuerza físicamente las partículas a unirse, ayudando a los procesos de difusión y unión en los límites de las partículas.
Esta sinergia reduce drásticamente la temperatura y el tiempo de sinterización necesarios para lograr la densidad total, a menudo requiriendo solo una décima parte de la presión utilizada en el prensado en frío.
Las ventajas clave de la sinterización por prensado en caliente
El mecanismo único del prensado en caliente se traduce directamente en una serie de beneficios distintos para el producto final y el propio proceso de fabricación.
Lograr una densidad casi teórica
La combinación de calor y presión es excepcionalmente eficiente para eliminar la porosidad. Esto permite la creación de piezas sinterizadas que se acercan al 100% de su densidad teórica.
Esta alta densidad está directamente relacionada con una resistencia mecánica superior y propiedades eléctricas mejoradas.
Menores temperaturas y uso de energía
Debido a que la presión ayuda al proceso de densificación, las temperaturas requeridas son significativamente más bajas que en la sinterización sin presión. Esto reduce el consumo total de energía y el tiempo de procesamiento.
Control del crecimiento del grano
Un desafío importante en la metalurgia y la cerámica es que las altas temperaturas mantenidas durante largos períodos pueden hacer que los granos internos del material crezcan. Los granos grandes a menudo conducen a una reducción de la resistencia y la tenacidad.
Los ciclos más cortos y las temperaturas más bajas del prensado en caliente inhiben eficazmente este crecimiento del grano, preservando una estructura interna fina y fuerte.
Creación de formas complejas y precisas
El proceso permite la producción de productos complejos y de tamaño preciso. Debido a que la pieza se forma y solidifica en un solo paso dentro de un molde, puede crear objetos casi con forma final que requieren un procesamiento posterior mínimo.
Comprendiendo las compensaciones
Aunque potente, la sinterización por prensado en caliente no es una solución universal. Una evaluación objetiva requiere comprender sus limitaciones prácticas.
Complejidad del proceso y del equipo
La maquinaria necesaria para aplicar de forma segura altas temperaturas y una presión mecánica significativa al mismo tiempo es inherentemente más compleja y especializada que un horno estándar o una prensa sola. Esto puede representar una inversión inicial notable.
Limitaciones geométricas
El proceso se basa en un molde para contener el polvo y aplicar presión. Si bien es capaz de crear formas complejas, se limita a geometrías que pueden prensarse y expulsarse con éxito de un molde. Esto es más restrictivo que los métodos de fabricación aditiva como la inyección de aglutinante.
Consideraciones sobre el tiempo de ciclo
Si bien la fase de sinterización es rápida, el tiempo total del ciclo —incluida la carga del polvo, el calentamiento del molde, el prensado, el enfriamiento y la expulsión de la pieza— puede ser más largo que el de algunos métodos de fabricación de alto volumen. Esto a menudo lo hace más adecuado para componentes de alto valor que para piezas producidas en masa.
Tomar la decisión correcta para su objetivo
La selección de un proceso de fabricación depende completamente de las prioridades específicas de su proyecto.
- Si su enfoque principal es la máxima densidad y el rendimiento del material: La sinterización por prensado en caliente es una opción excepcional para crear piezas con porosidad mínima y una estructura de grano fino, lo que lleva a una resistencia superior.
- Si su enfoque principal es trabajar con metales o cerámicas de alto punto de fusión: Este proceso es muy eficaz, ya que evita los costos energéticos extremos y los desafíos técnicos de intentar fundir y colar estos materiales.
- Si su enfoque principal es la producción de muy alto volumen y bajo costo: Debe evaluar cuidadosamente los tiempos de ciclo y los costos del equipo, ya que otros métodos como la metalurgia de polvos convencional podrían ser más económicos a escala.
En última instancia, elegir la sinterización por prensado en caliente es una decisión estratégica para priorizar la calidad y el rendimiento del material final.
Tabla resumen:
| Característica | Beneficio |
|---|---|
| Calor y presión simultáneos | Reduce la temperatura y el tiempo de procesamiento requeridos |
| Densidad casi teórica | Resistencia mecánica superior y propiedades mejoradas |
| Crecimiento de grano controlado | Preserva una estructura interna fina y fuerte |
| Formas netas complejas | Crea componentes precisos con un procesamiento posterior mínimo |
¿Necesita crear componentes de alto rendimiento con porosidad mínima?
KINTEK se especializa en equipos de laboratorio avanzados, incluidas soluciones de sinterización, para ayudarle a lograr una densidad y un rendimiento superiores del material. Nuestra experiencia respalda las necesidades precisas de los laboratorios que trabajan con cerámicas, metales y compuestos avanzados.
Contacte hoy mismo a nuestros expertos para discutir cómo nuestras soluciones pueden mejorar sus procesos de I+D y fabricación.
Guía Visual
Productos relacionados
- Horno de Prensado en Caliente al Vacío Máquina de Prensado al Vacío Calentado
- Horno de Prensado en Caliente al Vacío Máquina de Prensado al Vacío Horno Tubular
- Horno de Sinterización y Tratamiento Térmico al Vacío con Presión de Aire de 9MPa
- Prensa Hidráulica Manual de Alta Temperatura con Placas Calefactoras para Laboratorio
- Máquina de prensa hidráulica calentada con placas calentadas para prensa en caliente de laboratorio de caja de vacío
La gente también pregunta
- ¿Cómo afecta el entorno de vacío en un horno de prensado en caliente al sinterizado de carburos? Lograr una densidad relativa del 98%+
- ¿Por qué es crucial un control preciso de la temperatura en un horno de prensa en caliente al vacío? Dominando los compuestos de fibra de carbono y aluminio
- ¿Por qué se requiere un horno de prensado en caliente al vacío para aleaciones amorfas a granel de Ni-Zr-Ti-Si? Asegura la densificación de alta pureza
- ¿Cuáles son las funciones clave de un horno de sinterización de prensado en caliente al vacío? Producir pellets cerámicos de UN de alta densidad
- ¿Cómo impacta el control programado de temperatura de un horno de sinterización por prensado en caliente al nanocopper? Domina la Microestructura
- ¿Cómo contribuye un horno de prensado en caliente al vacío a la densificación de cerámicas de solución sólida (Ti,M)3AlC2?
- ¿Por qué el equipo de prensado en caliente al vacío puede reemplazar el prensado en frío? Mejora la eficiencia de producción de la aleación CuCr50
- ¿Qué es la sinterización en caliente? Logre una densidad y resistencia superiores para sus materiales



















