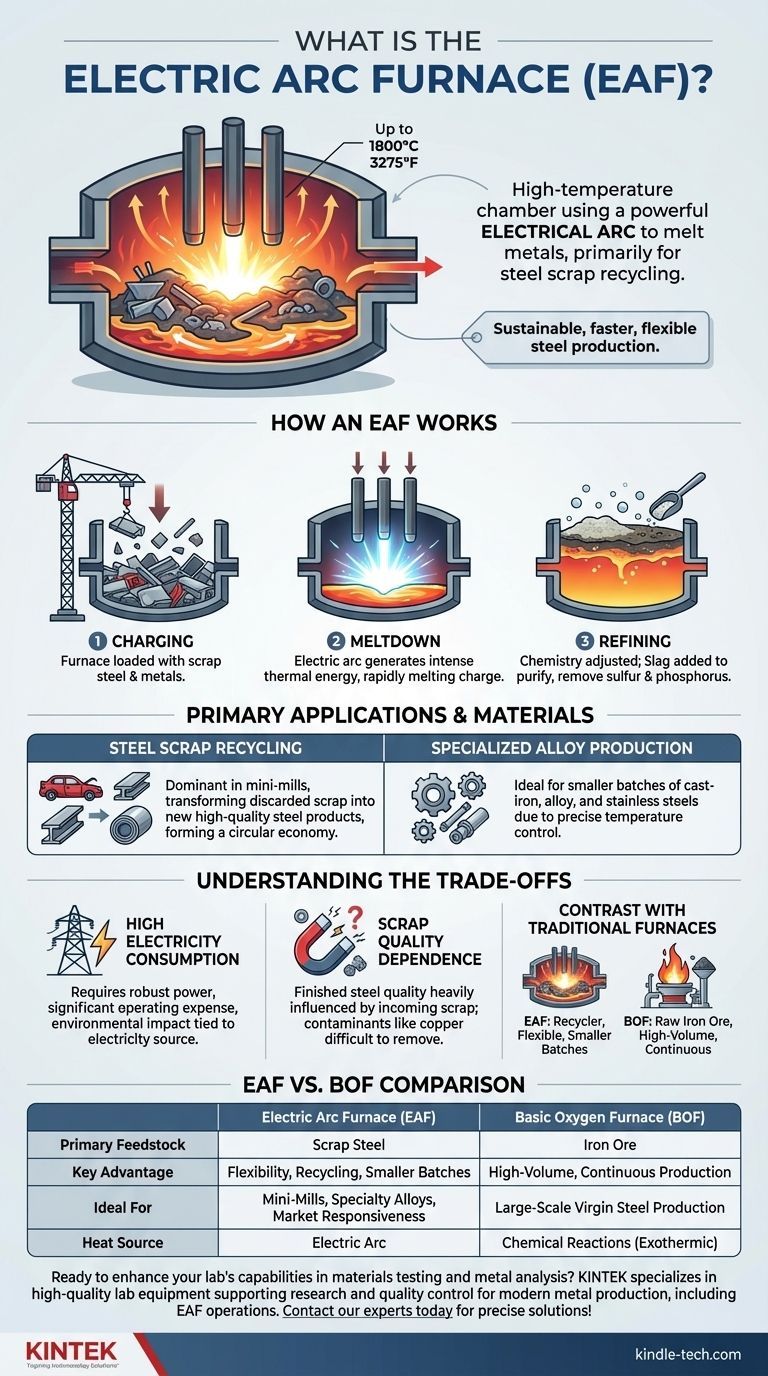
En esencia, un horno de arco eléctrico (HAE) es una cámara de alta temperatura que utiliza un potente arco eléctrico para fundir metales. Este proceso se utiliza principalmente para reciclar chatarra de acero, transformándola en nuevos productos de acero de alta calidad mediante la generación de un calor inmenso —hasta 1800°C (3275°F)— a través de una descarga de plasma controlada.
El horno de arco eléctrico es una piedra angular del reciclaje moderno. Evita la necesidad de mineral de hierro en bruto al usar electricidad para fundir y refinar de manera eficiente la chatarra existente, lo que lo convierte en un método de producción de acero más rápido, más flexible y, a menudo, más sostenible.

Cómo funciona un horno de arco eléctrico
El funcionamiento de un HAE es un proceso de varias etapas que aprovecha la intensa energía de la electricidad para convertir el metal sólido en un líquido fundido y refinable.
El principio del arco eléctrico
La fuente de calor no es una llama, sino un arco eléctrico. Se trata de una descarga de plasma sostenida, esencialmente una chispa continua de alta energía, que se forma entre los electrodos de grafito y la carga metálica dentro del horno.
Este arco convierte la energía eléctrica en energía térmica intensa, creando una bolsa de plasma que funde rápidamente la chatarra metálica con la que entra en contacto.
El proceso de fusión paso a paso
El horno opera en una secuencia distinta para asegurar una fusión y purificación eficientes.
-
Carga: El proceso comienza cargando el horno, típicamente desde la parte superior, con una mezcla cuidadosamente seleccionada de chatarra de acero y otros metales.
-
Fusión: Los grandes electrodos de grafito se bajan al horno. Se aplica un alto voltaje, lo que provoca un arco entre los electrodos y la chatarra. El calor resultante comienza a fundir rápidamente la carga de arriba hacia abajo.
-
Refinación: Una vez que el metal está fundido, se ajusta la química. Se añaden materiales como cal viva para formar una capa de escoria sobre el metal fundido. Esta escoria actúa como agente purificador, extrayendo impurezas como el azufre y el fósforo del acero.
Aplicaciones y materiales principales
Aunque versátil, el HAE es dominante en áreas específicas de la producción de metales debido a sus características únicas.
Reciclaje de chatarra de acero
La aplicación más significativa del HAE se encuentra en las "mini-acerías" que se centran en el reciclaje. Permite a los productores crear nuevos productos de acero directamente a partir de coches viejos, acero estructural y otras fuentes desechadas, formando un ciclo crítico en la economía circular.
Producción de metales y aleaciones especializadas
Más allá del acero al carbono, los HAE también se utilizan para producir productos de hierro fundido, aceros aleados y aceros inoxidables. Su control preciso de la temperatura y el tamaño de lote más pequeño los hacen ideales para crear grados de metal especializados.
Comprendiendo las ventajas y desventajas
El HAE no es una solución universal. Sus ventajas en flexibilidad y reciclaje vienen con consideraciones operativas específicas.
Alto consumo de electricidad
El principal inconveniente es su inmensa demanda de electricidad. Un HAE requiere una red eléctrica robusta y fiable, y los costos de electricidad representan una parte importante de sus gastos operativos. La huella ambiental del horno está, por lo tanto, directamente ligada a cómo se genera esa electricidad.
Dependencia de la calidad de la chatarra
La calidad del acero terminado está fuertemente influenciada por la calidad de la chatarra entrante. Los contaminantes en la chatarra (como el cobre o el estaño) pueden ser difíciles de eliminar y pueden afectar las propiedades del producto final, lo que requiere una cuidadosa selección y gestión de la chatarra.
Contraste con los hornos tradicionales
A diferencia de un horno de oxígeno básico (HOB), que utiliza principalmente mineral de hierro en bruto y produce su propio calor a través de reacciones químicas, un HAE es un reciclador. Un HOB es adecuado para la producción masiva y continua de acero virgen, mientras que un HAE sobresale en la producción por lotes más pequeña y flexible a partir de chatarra.
Cómo aplicar esto a su objetivo
Su elección de tecnología de horno depende completamente de su estrategia de producción, las materias primas disponibles y el enfoque del mercado.
- Si su enfoque principal es el reciclaje y la capacidad de respuesta del mercado: El HAE es la elección definitiva por su capacidad para procesar rápida y eficientemente chatarra de acero en nuevos productos.
- Si su enfoque principal es la producción de alto volumen a partir de materias primas: Un horno de oxígeno básico es más adecuado para la conversión a gran escala de mineral de hierro en acero.
- Si su enfoque principal es la creación de aleaciones especializadas en lotes más pequeños: El HAE proporciona el control de proceso y la flexibilidad necesarios para la fabricación de acero especial y hierro fundido.
En última instancia, el horno de arco eléctrico representa una tecnología fundamental que permite un enfoque más ágil y sostenible para la producción moderna de metales.
Tabla resumen:
| Aspecto | Horno de Arco Eléctrico (HAE) | Horno de Oxígeno Básico (HOB) |
|---|---|---|
| Materia prima principal | Chatarra de acero | Mineral de hierro |
| Ventaja clave | Flexibilidad, Reciclaje, Lotes más pequeños | Producción de alto volumen, Continua |
| Ideal para | Mini-acerías, Aleaciones especiales, Capacidad de respuesta del mercado | Producción de acero virgen a gran escala |
| Fuente de calor | Arco eléctrico | Reacciones químicas (Exotérmicas) |
¿Listo para mejorar las capacidades de su laboratorio en pruebas de materiales y análisis de metales? KINTEK se especializa en proporcionar equipos de laboratorio y consumibles de alta calidad que respaldan los procesos de investigación y control de calidad esenciales para la producción moderna de metales, incluidas las operaciones de hornos de arco eléctrico. Nuestras herramientas confiables le ayudan a lograr resultados precisos. ¡Contacte a nuestros expertos hoy para encontrar las soluciones perfectas para las necesidades de su laboratorio!
Guía Visual
Productos relacionados
- Horno de Tubo de Laboratorio de Alta Temperatura de 1400℃ con Tubo de Alúmina
- Horno de tubo de laboratorio vertical
- Horno Tubular de Laboratorio de Alta Temperatura de 1700℃ con Tubo de Alúmina
- Horno de Mufla de Laboratorio con Elevación Inferior
- Horno de Fusión por Inducción al Vacío para Fusión por Inducción
La gente también pregunta
- ¿Cómo colaboran un reactor de tubo de cuarzo y un horno de atmósfera en la pirólisis de Co@NC? Síntesis de Precisión Maestra
- ¿Cómo facilita un horno tubular de alta temperatura la transformación de fase de los productos de alúmina? Domine el control térmico
- ¿Por qué se utiliza un horno de tubo de cuarzo en la oxidación térmica de recubrimientos de MnCr2O4? Desbloquee la oxidación selectiva precisa
- ¿Qué precauciones se deben tomar al usar un horno tubular? Garantice un procesamiento seguro y eficaz a alta temperatura
- ¿Qué materiales se utilizan para los tubos en los hornos de tubo? Una guía para seleccionar el tubo adecuado para su proceso



















